Passwords have been the first line of defence in enterprise security since the beginning; they were the original single-factor authentication method. However, as cyber threats evolved, passwords have become the weakest link in defence against various types of attacks threatening the security of enterprise digital infrastructure.
Even after the advent of layered controls like MFA, attackers continue to focus on credential-based attacks. Data from Check Point External Risk Management reveals a staggering 160% increase in compromised credentials in 2025 compared to 2024. No wonder credential-based attacks remain one of the most common entry points for breaches, even in mature environments, and phishing, password reuse, and credential stuffing continue to undermine enterprise access security.
Therefore, organizations are looking to evolve beyond passwords and traditional MFA, increasingly adopting passwordless authentication. Enterprise passwordless authentication completely removes passwords from the authentication flow and replaces them with stronger, phishing-resistant methods. Secure access management is crucial to protecting the enterprise’s digital infrastructure; passwordless authentication enables that by aligning closely with zero-trust principles and significantly improving credential theft prevention.
This article explains passwordless authentication, how it works, and how it strengthens MFA, Zero Trust, and enterprise security. It also covers deployment strategies and the role of enterprise IAM platforms in enabling secure, scalable passwordless access.

What Is Passwordless Authentication?
Before understanding passwordless authentication, it is crucial to revisit multifactor authentication and how it enforces layers of security that incorporate user identity verification methods to complement password verification.
Passwords are shared secrets that can be leaked or obtained through fraudulent means, such as phishing. MFA aims to address weaknesses in password authentication by requiring users to prove their identity. Though it offers additional layers of security, password-based authentication remains vulnerable. So, eliminating passwords completely is the key to securing your IT infrastructure, and passwordless authentication makes that possible.
Passwordless authentication is an authentication model that enables user identity verification without entering a password. Passwordless verification replaces passwords with unique, non-reusable credentials tied to a user and device. Instead of asking for a password, a passwordless login demands cryptographic proof, device trust, or inherent user factors, so attackers cannot easily steal, reuse, or phish. This makes passwordless security fundamentally stronger.
How does Passwordless Authentication Work?
Passwordless authentication works based on the underlying technology of public-key cryptography. Which follows these steps to authenticate a user and enable access.
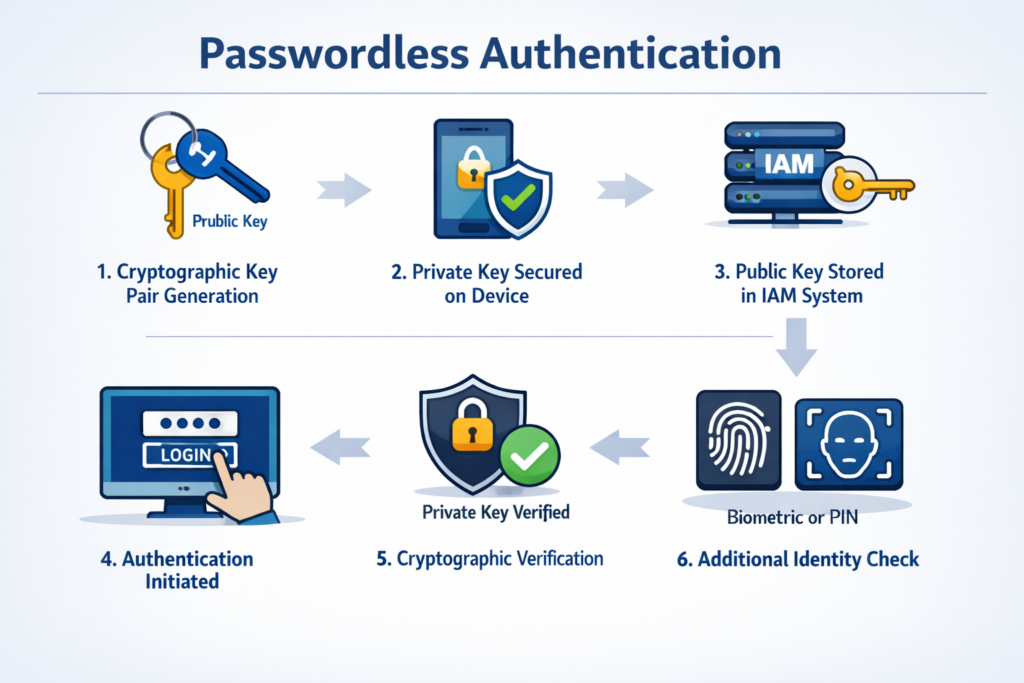
- A cryptographic key pair is generated when a user enrolls.
- The user device securely stores a private key.
- The Identity and Access Management (IAM) system, or the concerned service, stores a public key.
- The authentication process is initiated.
- The cryptographic authentication method proves the user’s possession of the private key.
- A local verification method, such as biometrics or device PINs, complements the user identity verification.
This authentication method is device-based, and so, private credentials are never transmitted, making attacks like phishing ineffective.
Benefits of Passwordless Authentication for Enterprises
For enterprises, passwordless authentication is both a security upgrade and a productivity enabler. Passwordless authentication empowers enterprise security with:
- Significantly better Phishing resistance
- Reduced attack surface
- Effective credential theft prevention
- Improved user experience
- Reduced helpdesk overhead
- Compliance with GDPR, SOC2, and ISO27001 standards
Passwordless Authentication vs MFA: How They Work Together
Passwordless authentication and MFA serve the same purpose: authenticating users, verifying their identities, and granting access. However, they are not the same.
Traditional multifactor authentication complements password verification with multiple factors. In contrast, passwordless MFA completely removes passwords while retaining multiple factors, including device possession and biometrics.
Passwordless authentication can be combined with adaptive MFA and risk-based authentication, just like traditional MFA. The system dynamically adjusts controls based on user behavior, device trust, and context, prompting the user to provide additional factors when required.
Passwordless Authentication Methods and Technologies
Modern passwordless authentication solutions rely on open standards and secure hardware.
Open standards are publicly specified and are open for scrutiny for flaws; they are vendor-neutral, interoperable, and supported across browsers, operating systems, and IAM platforms. They can be integrated into existing IAM and SSO systems and scaled seamlessly.
Secure hardware isolates private keys from the OS and protects them from phishing, theft, and remote attacks. It also aligns with compliance frameworks such as ISO27001, SOC2, GDPR, and Zero Trust principles.
To enable scalable passwordless access control across diverse enterprise environments, passwordless authentication employs:
- Passkeys based on FIDO2 and WebAuthn
- Biometric authentication, including fingerprints, facial recognition, and retinal scans
- Hardware security keys that connect through USB, NFC, or Bluetooth
- Mobile-based passwordless login using trusted devices and cryptographic challenges
Passwordless Deployment Strategy and Best Practices
A successful passwordless deployment requires careful planning and a gradual transition. Implementing it effectively and achieving faster adoption and better outcomes requires following the proven passwordless best practices, which include:
- Planning a phased passwordless journey segmented by user group and risk profile
- Smooth passwordless integration with legacy and cloud applications
- Creating a passwordless strategy to meet Zero Trust and secure access management goals
Passwordless Authentication and Enterprise IAM Platforms
Scaling passwordless authentication requires robust IAM platforms with passwordless support. By integrating passwordless authentication into identity and access management (IAM), you can completely eliminate the need for passwords while ensuring consistent enterprise access security across users, applications, and environments.
IAM platforms with passwordless support:
- Centralize identity.
- Enforce policy-driven access.
- Integrate passwordless methods with SSO, adaptive controls, and device trust.
Final Thoughts
It is time for enterprises to move away from vulnerable passwords to passwordless authentication, as it completely changes the fundamentals of securing access using cryptographic, phishing-resistant identity verification. Moreover, compromised passwords create an expanded attack surface; eliminating passwords can significantly reduce it while improving the user experience and operational efficiency.
Passwordless authentication bolsters enterprise security when implemented through the right IAM platforms and aligned with MFA, adaptive controls, and Zero Trust principles. When implemented properly, it becomes a strategic enabler of enterprise access security, delivering stronger protection, better compliance, and a future-ready authentication model.
FAQs
1. Is passwordless authentication MFA?
Passwordless authentication can be MFA when it combines multiple factors, such as device possession and biometrics, without passwords. It often delivers stronger security than traditional MFA.
2. How to enable passwordless MFA?
You can enable passwordless MFA by deploying FIDO2, passkeys, or biometrics via IAM platforms that support passwordless authentication, and by integrating adaptive policies and secure device-based authentication.
3. What is the difference between passwordless sign-in and push MFA?
Passwordless sign-in uses cryptographic authentication without passwords, while push MFA still relies on passwords plus approvals, making it more vulnerable to phishing attacks.
4. What are the disadvantages of passwordless authentication?
Challenges in passwordless authentication include device dependency, recovery scenarios, legacy system integration, and user onboarding, but these are manageable with proper passwordless deployment planning.


